Prevention and Control Measure of COVID-19
in China
Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention
March 12
nd
, 2020
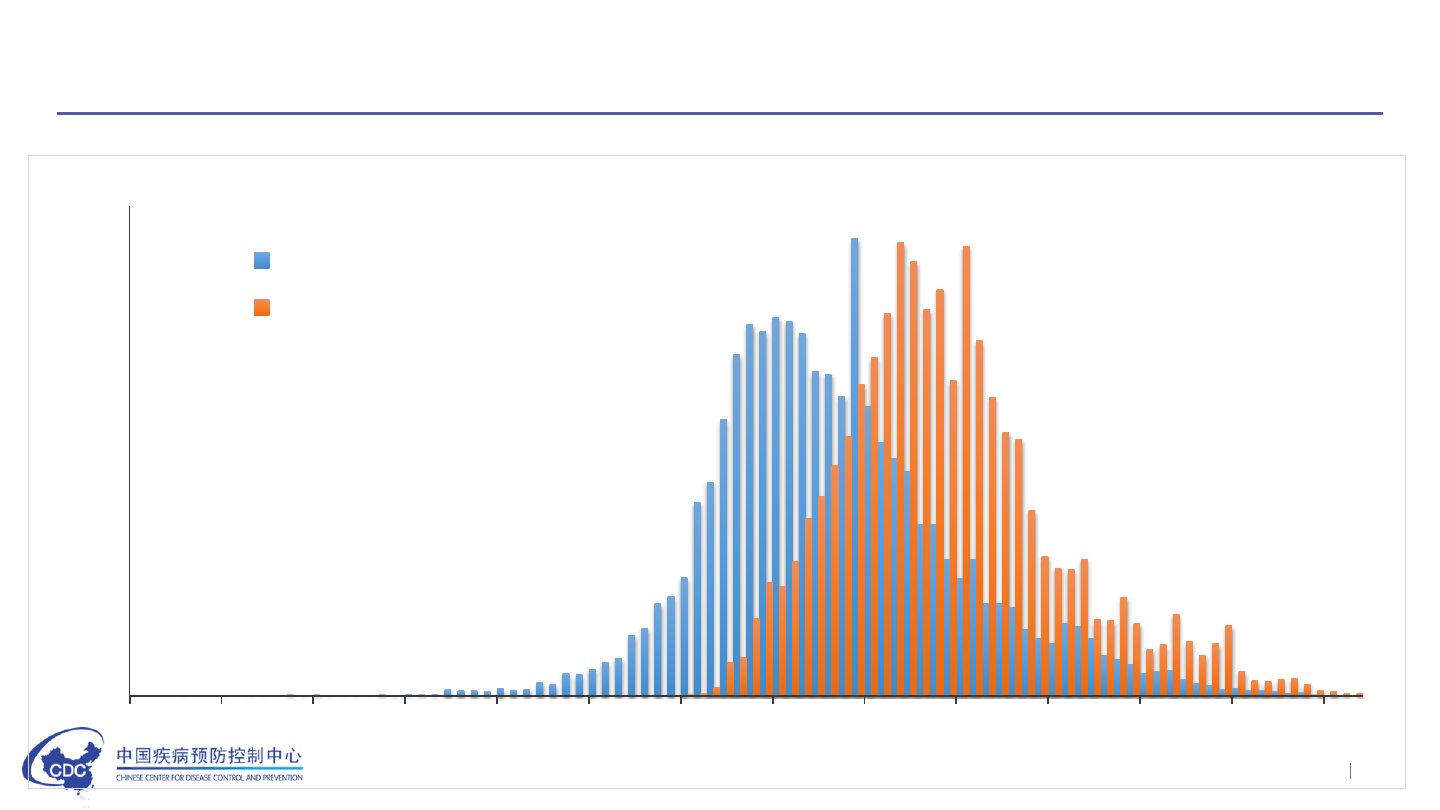
Epidemic curve of COVID-19 in China
( as of March 10, 2020)
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
3500
4000
12-8
12-15
12-22
12-29
1-5
1-12
1-19
1-26
2-2
2-9
2-16
2-23
3-1
3-8
Cases
Confirmed Cases (80,778)
date of onset
date of report

Preliminary understanding of disease features
• Transmission capacity
• COVID-19 is mainly transmitted through contact with respiratory droplets
• Majority of onwards transmission is occurring around the time of illness onset in an
infected person, and likely pre-symptomatic transmission was also identified.
• R
0
: 2-3, serial interval: 6 days.
• Incubation periods: 1-14 days
• Secondary incidence rate: 5% (symptomatic transmission), 0.6%(asymptomatic
transmission)
• Disease severity
• About 80% are mild/moderate, 15% severe, 5% critical
• Case fatality risk: about 6% in Wuhan city, 0.8% other areas
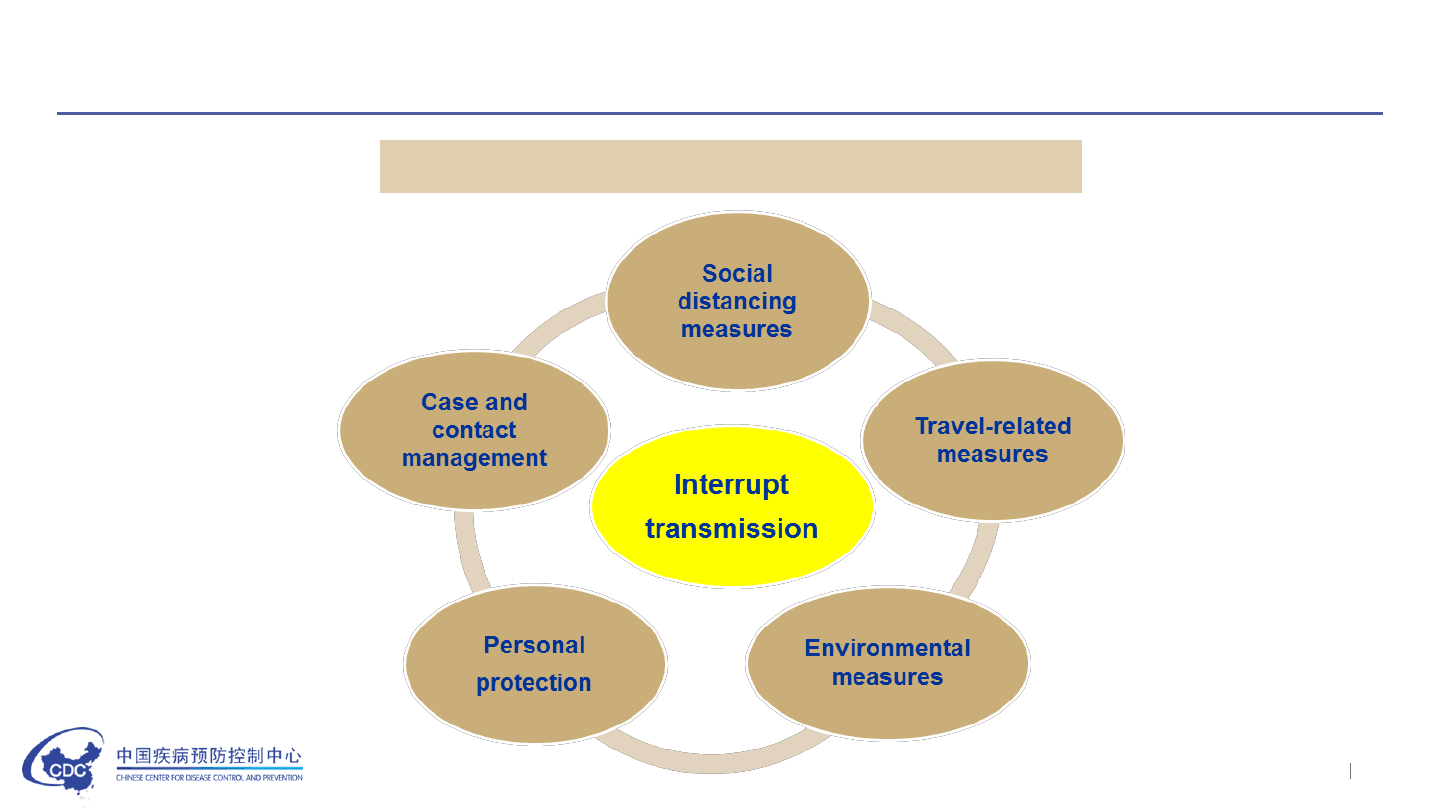
Containment Strategy in China
Non-pharmaceutical intervention measures

Tailored control measures at varied risk levels
• Low-risk areas: strictly prevent importation.
• Medium-risk areas: to prevent importation and stop local transmission.
• High-risk areas: to stop local transmission, prevent exportation, and
implement strict prevention and control measures.
• Timely risk levels adjustment mechanism.
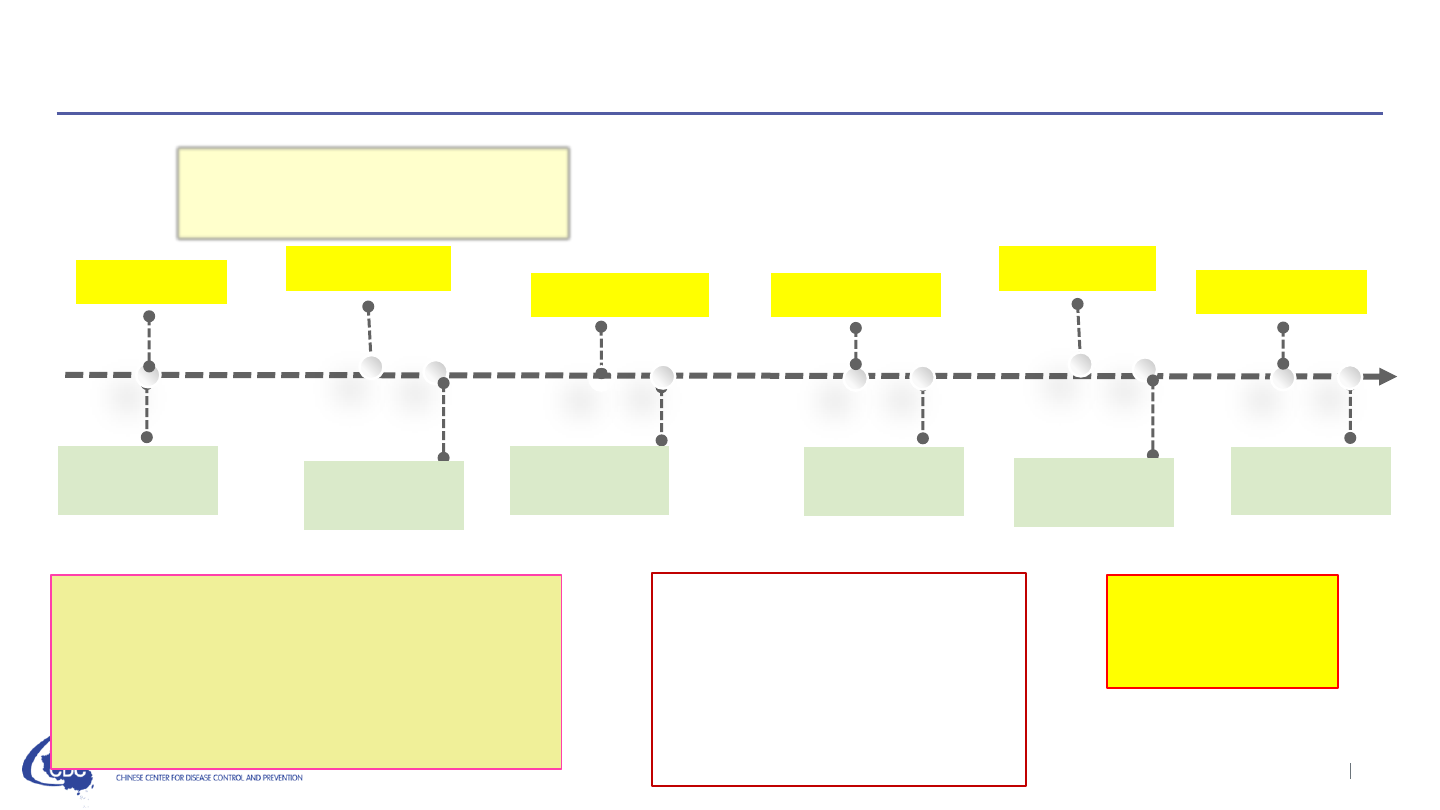
National prevention and control guidelines for COVID-19
Jan 20
statutory infectious disease
management
Jan 15th
Version I
Jan 28
Version II
Feb 6
Version III Version IV
Nationwide
training
Jan 22
Nationwide
training
Nationwide
training
Nationwide
training
Jan 30
Feb 8
Components:
• Case detection and management
• Case and cluster investigation
• Contact tracing and management
• Laboratory testing
• PPE and disinfection
Feb 21
Version V
Nationwide
training
Feb 22
Mar 7
Version VI
Nationwide
training
Mar 10
Four E key measures:
Early detection
Early reporting
Early isolation
Early treatment
Rapid
detection &
response
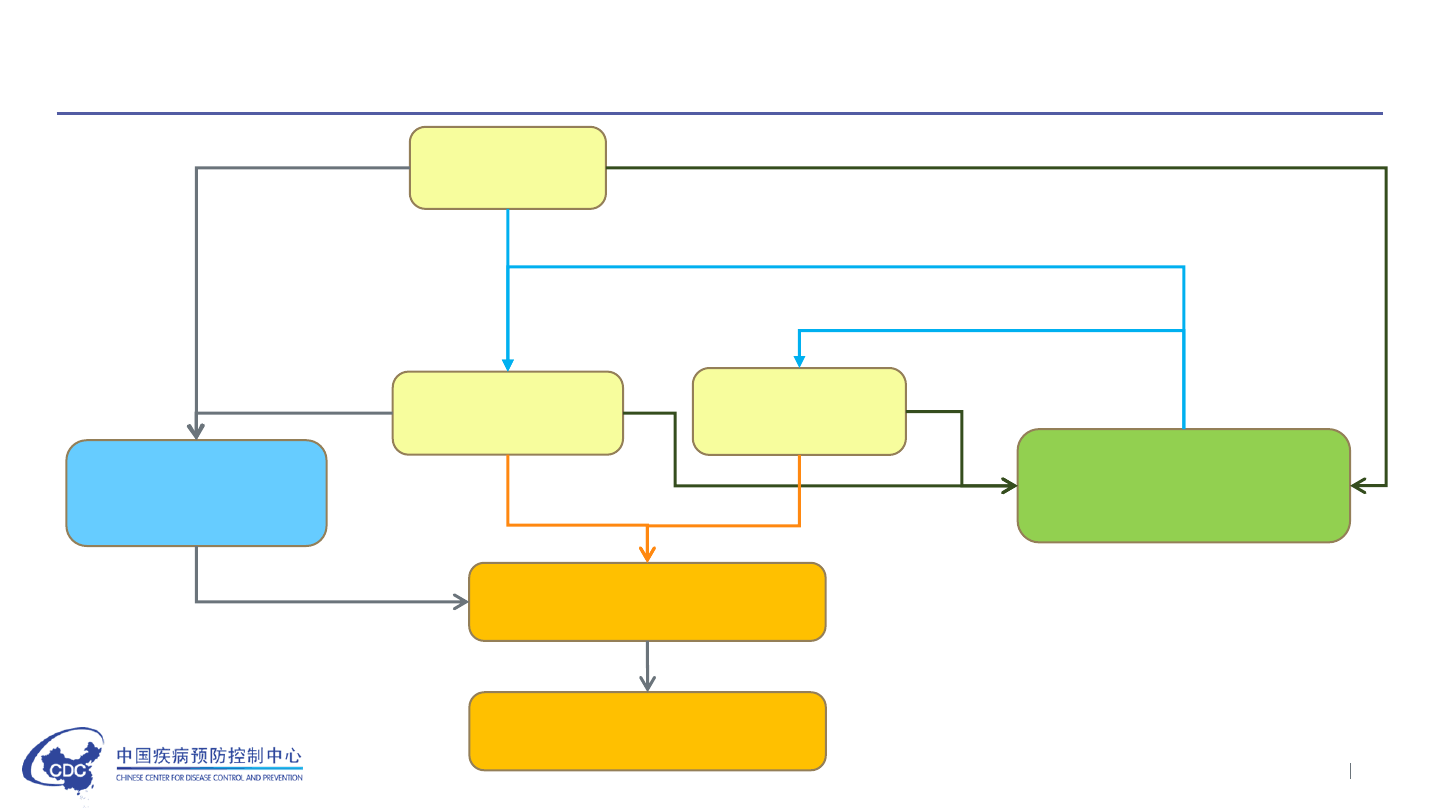
Case & contact detection and management workflow
Suspected
Cases
Confirmed
cases
Case treatment
and management
Isolation
Close contact tracing
and medical observation
Asymptomatic
infection
Lab test
Discharge or decease
Lab test
Lab test
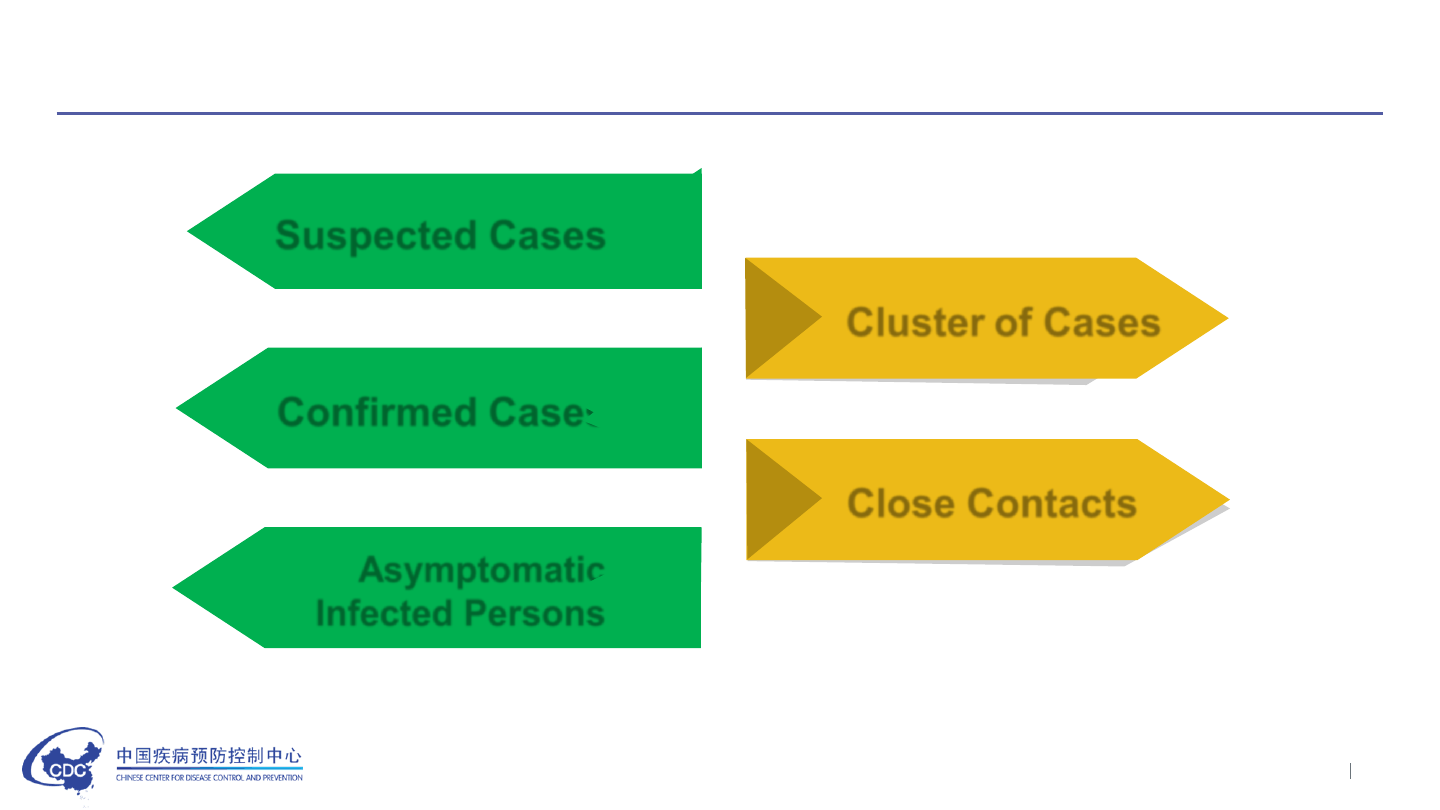
Surveillance case definitions
Cluster of Cases
04
Suspected Cases
01
Close Contacts
05
Confirmed Cases
02
Asymptomatic
Infected Persons
03
The latest English version of guidelines will be published soon in China CDC Weekly journal.

Early and active detection of cases
Healthcare facilities at all levels
Existing surveillance networks for PUE, ILI and SARI
Health status monitoring of close contacts
Port health quarantine for the imported cases detection
Primary level organizations or employers
1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
Case reporting requirement
• Suspected cases, confirmed cases, or asymptomatic infected
individuals were required to report
• Web-based reporting system within 2h after diagnosis
• Information checking by CDCs within 2h after receiving the report
Case reporting
• When suspected cases confirmed or excluded
• When clinical severity changed with the progression of illness
• When status of asymptomatic infected individuals changed
• when died of COVID-19, date of death need to be updated
Updating reports
• The first COVID-19 confirmed case or cluster in a county/district
• Web-based emergency events reporting system within 2h
• The emergency level should be updated based on investigation
findings and assessments
Reporting of
public health events
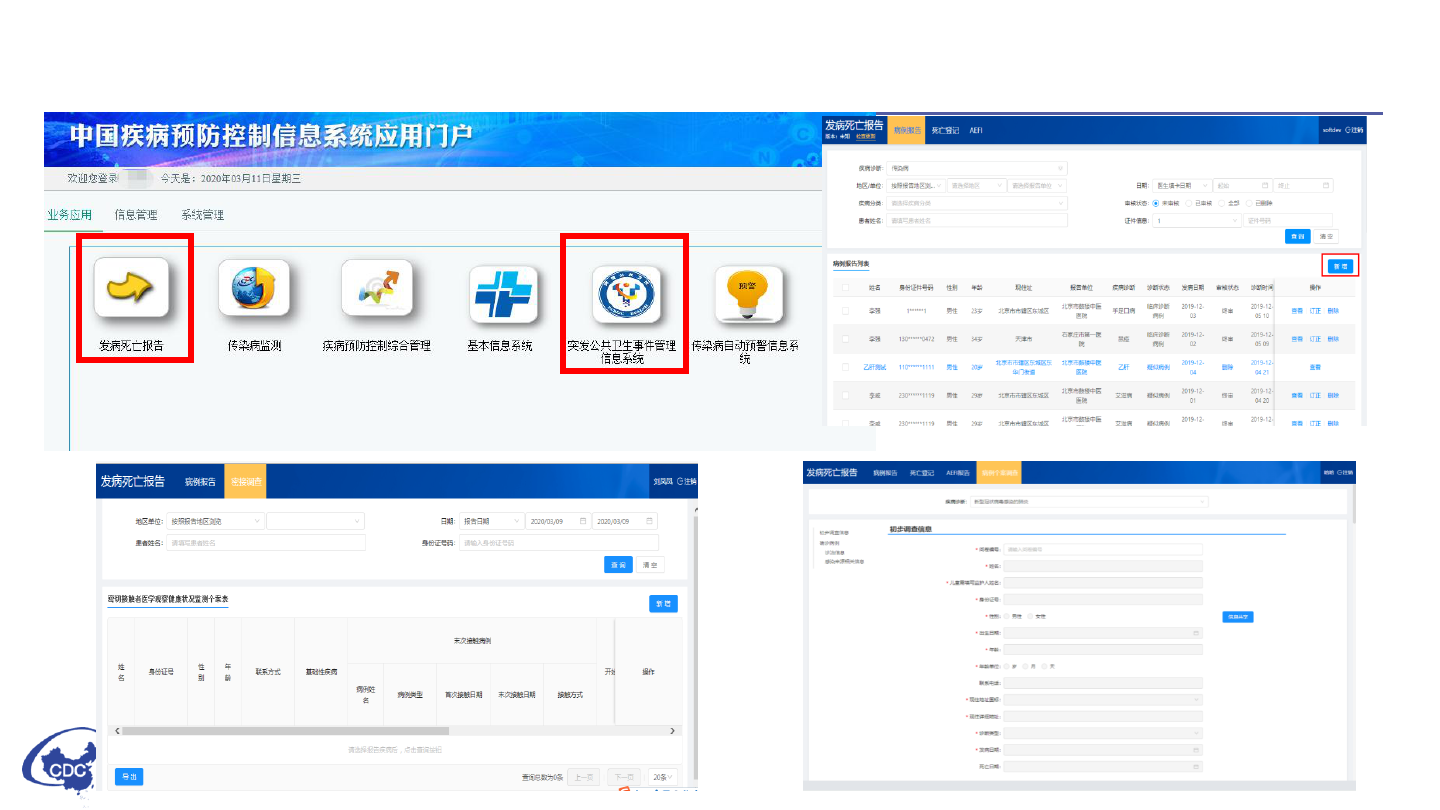
Chinese Web-based Reporting System
The Platform for Cases and Emergency Events
Reporting
Notifiable Individual Case
Information System
Close Contacts Tracing and
Management System
Epidemiological Investigation information
System

Case management
• Isolation and treatment at designated hospitals
• Suspected cases should be isolated in a single room.
• Confirmed cases and asymptomatic infection could be isolated in a
same room.

Case discharge criteria
• Suspected cases could be discharged only after their nucleic acid testing are
negative for respiratory pathogen twice consecutively (sampling interval being at
least one day), and both IgM and IgG antibody test are negative 7 days since
illness onset.
• Asymptomatic cases could be discharged only after their nucleic acid testing
are negative for respiratory pathogen twice consecutively (sampling interval being
at least one day).
• Confirmed cases could be discharged when meeting with the following criteria:
• body temperature is back to normal for more than three days;
• respiratory symptoms improve obviously;
• pulmonary imaging shows obvious absorption of inflammation;
• and nucleic acid tests negative for respiratory tract pathogen twice consecutively
(sampling interval being at least one day).

Contact tracing and management
• Close contact tracing
• Close contact: Any person who had contacted (within 1 meter) with a
confirmed or suspected case since the date of illness and two days before
illness onset, including:
• Any social or health care worker, who provided direct personal or health care of
a symptomatic confirmed case of 2019-nCoV or within the same closed setting
• Any person who has resided in the same household (or other closed setting) as
the cases
• Asympomatic infection’s contact: Any person who had contact (within 1
meter) with an asympomatic infection within 2 days before sampling.

Contact tracing and management
• Close contact management
• Perform medical observation at home or at designated places (i.e.
hotel) .
• Duration: 14 days from the last contact with the cases or asymptomatic
infection.
• Body temperature and health status examination are performed twice a
day by community health care workers.
• The unnecessary outdoor activities are not permitted, and living
accommodation is supplied by local community.

Specimen collection and lab testing
• Healthcare facilities receiving COVID-19 cases should collect relevant clinical
specimens timely.
• upper respiratory tract specimens
• lower respiratory tract specimens
• stool specimens/anal swab
• blood and serum specimens, etc.
• Feedback the test result within 12 hours
• Specimen collection, transportation, storage and testing should be conducted strictly
in accordance with the requirements set out in the lab testing protocol issued by
China CDC.
• Verification and confirmation
• All the original specimens of clusters with five or more COVID-19 cases in each region
• Oversea imported cases
China CDC has developed a total of 38 interim guidelines for the public population
Public health communication
General
population
• Hand hygiene
• Respiratory
etiquette
• Face masks
• Disinfection
• …
Special
group
• The elder
• Patients with
chronic
diseases
• Maternal
prevention
• Students
returning to
school after
winter vacation
• …
Specific
places
• Family
• Kindergarten (or
school)
• Nursing homes
• Private cars
• Subway and
bus
• Airline
• …
Personal
protection
• The selection and
use of masks
• How to deal with
these masks
• How to wash your
hands correctly?
• Home disinfection
• …
Travel-related
• Travel health
advice
• What should a
person with a
history of living
or traveling in
an endemic
area do?
• …
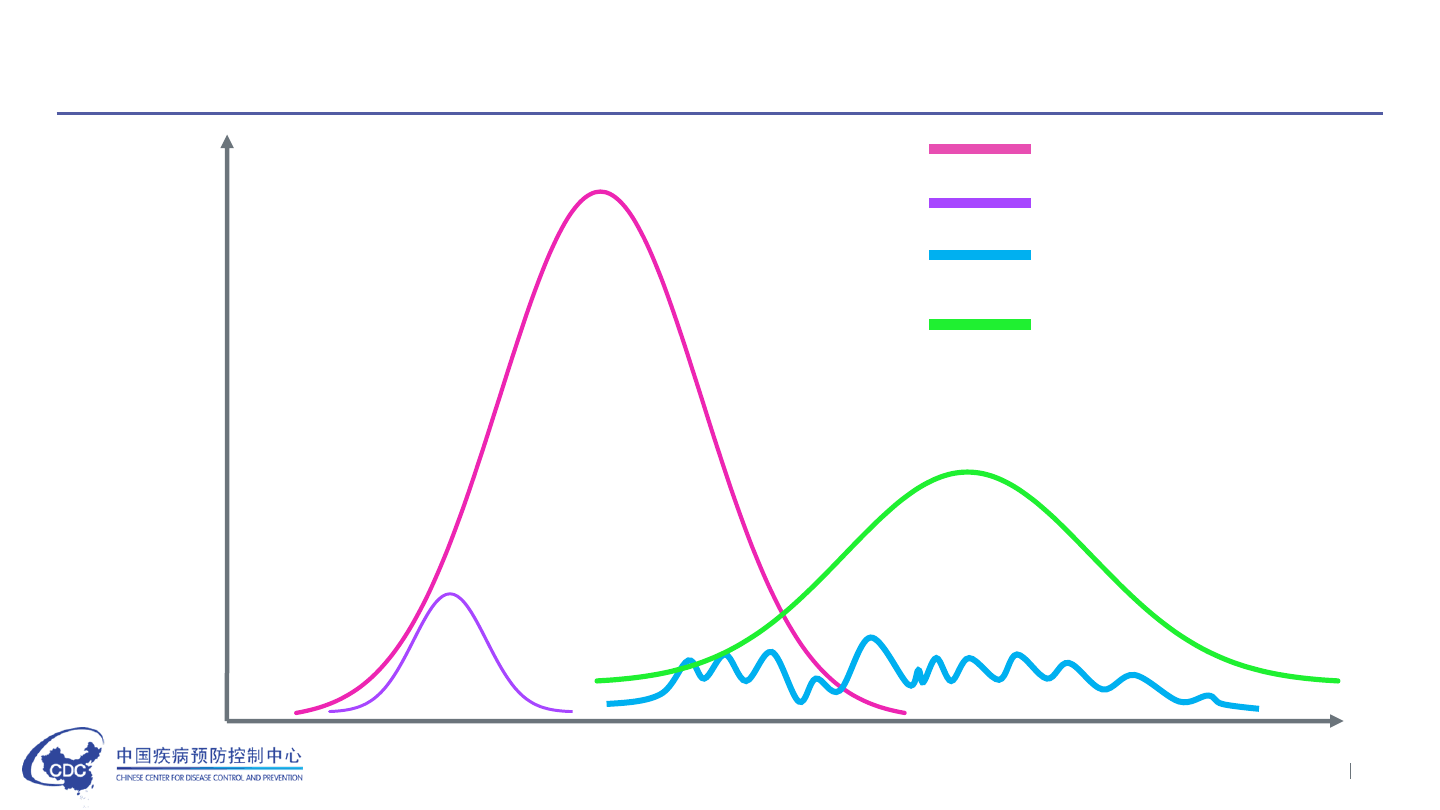
cases
Time
With no active intervention
Containment strategy
Oversea importation
control strategy
Mitigation strategy
Simulation scenario of epidemic with different response strategies

